What is Fibrosis?
Why Imaging?
Collagen Medical Solution
Approach
Indications and Preclinical Efficacy
Liver Fibrosis
Myocardial Fibrosis
Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Fibrosis is a hallmark of many major illnesses including heart failure, chronic liver diseases, pulmonary fibrosis, and many cancers
- Fibrosis is a scarring process resulting in increased extracellular matrix production, chiefly type I collagen
- The presence of fibrosis can be diagnostic, e.g. for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
- The extent of fibrosis is prognostic and a good indicator of disease progression or treatment efficacy
Why Imaging?
- Diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy monitoring
- Gold standard for assessment of fibrosis is biopsy
- Biopsy is invasive, carries real risks of morbidity and mortality, and typically cannot be performed repeatedly
- Alternate methods for assessing fibrosis suffer from poor sensitivity or specificity for disease and are of little use for disease staging
- Better tools are urgently needed for diagnosis, staging, and monitoring of therapy
Collagen Medical Solution
Approach
- Excess collagen can be imaged using a targeted small molecule MRI probe
- Broad utility across different diseases and organ systems
- MRI provides high spatial resolution and ability to quantify fibrosis locally and throughout the entire organ (unlike blood tests)
- No ionizing radiation (unlike PET, SPECT), and does not raise concerns of radiation burden in following disease progression in relatively healthy subjects on an annual/semi-annual basis
- Short peptides specific to type I collagen
- Optimized affinity, metabolic stability, and functionalization to enable imaging
- Lead probe CM-50 is high affinity, high avidity collagen binding peptide that is conjugated to three gadolinium (Gd) chelates for strong, positive MR signal enhancement
- Probes localize and are retained in areas of increased collagen deposition, resulting in a prolonged and selective enhancement of collagen rich tissue in an MRI scan thereby rendering a quantitative assessment of the extent of diseas
- Probes are relatively small (<5 kDa), renally excreted, and show no non-specific binding
- Additional expertise in MR acquisition and quantitative methods for fibrosis detection and disease staging
Indications and Preclinical Efficacy
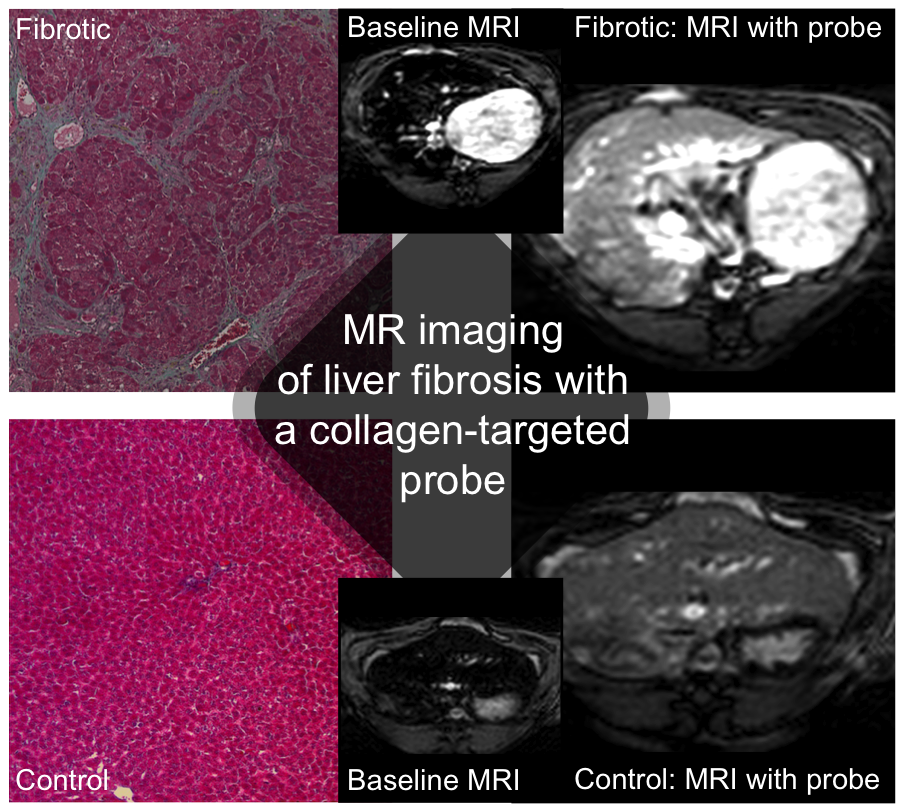
Liver Fibrosis
- Present in hepatitis C and B (HCV, HBV), alcoholic liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
- HCV affects 2% of the US population and accounts for the majority of liver transplants
- 8.5% of the population abuse or are dependent on alcohol and are at high risk for alcoholic liver disease
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is epidemic (driven by the rise in obesity, diabetes) with 17 – 33% of the US population afflicted.
- 30-50% of NAFLD patients will progress to (NASH), and this group is further at risk for progression to cirrhosis (15-25%), organ failure, liver cancer or death
Collagen probe CM-50 can detect and stage liver fibrosis in rodent models of disease

Myocardial Fibrosis
- Fibrosis is a key marker of adverse cardiac remodeling
- Strong correlation between the extent of fibrosis and the progression of congestive heart failure
- Diffuse fibrosis can lead to atrial arrhythmia (2.2 M patients) and ventricular arrhythmia (cause of 350,000 death/year)
- Myocardial fibrosis imaging test would serve a market of >4M
patients with heart arrhythmia, 5.8M in heart failure, in addition to
patients with ischemic heart disease, hypertropic cardiomyopathy and
dilated cardiomyopathie
CM-50 can detect and quantify extent of myocardial fibrosis in mouse model
Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other fibrotic diseases of the lung
- Replacement of normal lung with scar tissue causes irreversible decrease in oxygen diffusion capability
- Increased risk for pulmonary infection, pulmonary hypertension, heart failure
- 50,000 new cases diagnosed each year in the US, up to 40,000 deaths/year
CM-50 specifically identifies pulmonary fibrosis in mouse model of disease